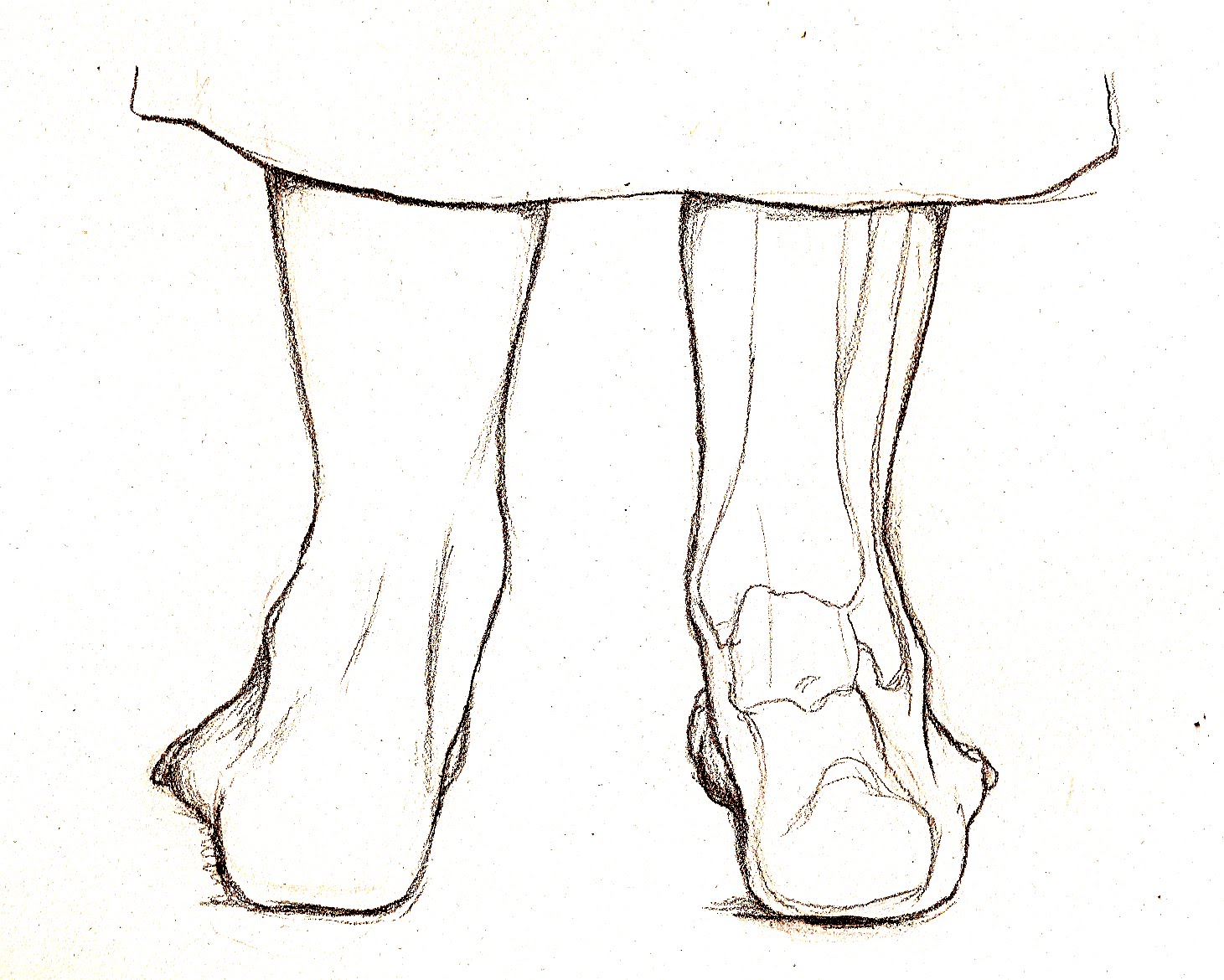
Overview

The loss of the arch of the foot (also known in some cases as the ?instep?) is called a flatfoot. People may have a very low arch or absolutely no arch whatsoever. Whilst most people with flat feet have been that way since a young age, in some people the arch height reduces over time. This can be due to systemic health concerns, degeneration of muscles and joints, hormonal changes or specific injury.
Causes
As discussed above, many health conditions can create a painful flatfoot. Damage to the posterior tibial tendon is the most common cause of AAFD. The posterior tibial tendon is one of the most important tendons of the leg. It starts at a muscle in the calf, travels down the inside of the lower leg and attaches to the bones on the inside of the foot. The main function of this tendon is to hold up the arch and support your foot when you walk. If the tendon becomes inflamed or torn, the arch will slowly collapse. Women and people over 40 are more likely to develop problems with the posterior tibial tendon. Other risk factors include obesity, diabetes, and hypertension. Having flat feet since childhood increases the risk of developing a tear in the posterior tibial tendon. In addition, people who are involved in high impact sports, such as basketball, tennis, or soccer, may have tears of the tendon from repetitive use.
Symptoms
Knee/Hip/Back Pain - When the arch collapses in the foot, it triggers a series of compensations up the joint chain, leading to increased stress on the knee, pelvis and low back. Plantar fasciitis - This condition is characterized by heel pain, especially with the first few steps you take. The plantar fascia stretches as the arch falls, putting stress on the heel. Bunions - If you see a bony bump developing at the base of your big toe, you are likely developing a bunion. It may be swollen, red or painful when it rubs against your shoe. A flattened arch spreads the forefoot and causes the big toe to deviate toward the second toe. Shin splints - This term generally refers to pain anywhere along the shinbone. It is typically due to overuse and is aggravated after exercise and activity.
Diagnosis
An examination of the foot is enough for the health care provider to diagnose flat foot. However, the cause must be determined. If an arch develops when the patient stands on his or her toes, the flat foot is called flexible and no treatment or further work-up is necessary. If there is pain associated with the foot or if the arch does not develop with toe-standing, x-rays are necessary. If a tarsal coalition is suspected, a CT scan is often ordered. If a posterior tibial tendon injury is suspected, your health care provider may recommend an MRI.
Why do arches fall?
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment isn't usually needed for flat feet because the condition doesn't usually cause any significant problems. Aching feet can often be relieved by wearing supportive shoes that fit properly. You may need to wear shoes that are wider than normal. If your feet overpronate, you may need to wear a special insole (an orthotic) inside your shoes to stop your feet rolling inwards when you walk or run. These will usually need to be made and fitted by a podiatrist. Stretching your calf and Achilles tendon may also help as a tight Achilles can make your foot overpronate. To stretch your calf and Achilles tendon, step forwards with your left leg and bend it, with your right leg straight and both feet pointing forwards, push your right heel into the ground while keeping your right leg straight; you should feel the stretch at the back of your right leg, below the knee, hold the stretch for 15 to 30 seconds and repeat with the opposite leg, repeat the stretch two to four times on each leg, and repeat the overall exercise three to four times a day.
Surgical Treatment
Rarely does the physician use surgery to correct a foot that is congenitally flat, which typically does not cause pain. If the patient has a fallen arch that is painful, though, the foot and ankle physicians at Midwest Orthopaedics at Rush may perform surgery to reconstruct the tendon and "lift up" the fallen arch. This requires a combination of tendon re-routing procedures, ligament repairs, and bone cutting or fusion procedures.
After Care
Time off work depends on the type of work as well as the surgical procedures performed. . A patient will be required to be non-weight bearing in a cast or splint and use crutches for four to twelve weeks. Usually a patient can return to work in one to two weeks if they are able to work while seated. If a person's job requires standing and walking, return to work may take several weeks. Complete recovery may take six months to a full year. Complications can occur as with all surgeries, but are minimized by strictly following your surgeon's post-operative instructions. The main complications include infection, bone that is slow to heal or does not heal, progression or reoccurrence of deformity, a stiff foot, and the need for further surgery. Many of the above complications can be avoided by only putting weight on the operative foot when allowed by your surgeon.

The loss of the arch of the foot (also known in some cases as the ?instep?) is called a flatfoot. People may have a very low arch or absolutely no arch whatsoever. Whilst most people with flat feet have been that way since a young age, in some people the arch height reduces over time. This can be due to systemic health concerns, degeneration of muscles and joints, hormonal changes or specific injury.
Causes
As discussed above, many health conditions can create a painful flatfoot. Damage to the posterior tibial tendon is the most common cause of AAFD. The posterior tibial tendon is one of the most important tendons of the leg. It starts at a muscle in the calf, travels down the inside of the lower leg and attaches to the bones on the inside of the foot. The main function of this tendon is to hold up the arch and support your foot when you walk. If the tendon becomes inflamed or torn, the arch will slowly collapse. Women and people over 40 are more likely to develop problems with the posterior tibial tendon. Other risk factors include obesity, diabetes, and hypertension. Having flat feet since childhood increases the risk of developing a tear in the posterior tibial tendon. In addition, people who are involved in high impact sports, such as basketball, tennis, or soccer, may have tears of the tendon from repetitive use.
Symptoms
Knee/Hip/Back Pain - When the arch collapses in the foot, it triggers a series of compensations up the joint chain, leading to increased stress on the knee, pelvis and low back. Plantar fasciitis - This condition is characterized by heel pain, especially with the first few steps you take. The plantar fascia stretches as the arch falls, putting stress on the heel. Bunions - If you see a bony bump developing at the base of your big toe, you are likely developing a bunion. It may be swollen, red or painful when it rubs against your shoe. A flattened arch spreads the forefoot and causes the big toe to deviate toward the second toe. Shin splints - This term generally refers to pain anywhere along the shinbone. It is typically due to overuse and is aggravated after exercise and activity.
Diagnosis
An examination of the foot is enough for the health care provider to diagnose flat foot. However, the cause must be determined. If an arch develops when the patient stands on his or her toes, the flat foot is called flexible and no treatment or further work-up is necessary. If there is pain associated with the foot or if the arch does not develop with toe-standing, x-rays are necessary. If a tarsal coalition is suspected, a CT scan is often ordered. If a posterior tibial tendon injury is suspected, your health care provider may recommend an MRI.
Why do arches fall?
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment isn't usually needed for flat feet because the condition doesn't usually cause any significant problems. Aching feet can often be relieved by wearing supportive shoes that fit properly. You may need to wear shoes that are wider than normal. If your feet overpronate, you may need to wear a special insole (an orthotic) inside your shoes to stop your feet rolling inwards when you walk or run. These will usually need to be made and fitted by a podiatrist. Stretching your calf and Achilles tendon may also help as a tight Achilles can make your foot overpronate. To stretch your calf and Achilles tendon, step forwards with your left leg and bend it, with your right leg straight and both feet pointing forwards, push your right heel into the ground while keeping your right leg straight; you should feel the stretch at the back of your right leg, below the knee, hold the stretch for 15 to 30 seconds and repeat with the opposite leg, repeat the stretch two to four times on each leg, and repeat the overall exercise three to four times a day.
Surgical Treatment

Rarely does the physician use surgery to correct a foot that is congenitally flat, which typically does not cause pain. If the patient has a fallen arch that is painful, though, the foot and ankle physicians at Midwest Orthopaedics at Rush may perform surgery to reconstruct the tendon and "lift up" the fallen arch. This requires a combination of tendon re-routing procedures, ligament repairs, and bone cutting or fusion procedures.
After Care
Time off work depends on the type of work as well as the surgical procedures performed. . A patient will be required to be non-weight bearing in a cast or splint and use crutches for four to twelve weeks. Usually a patient can return to work in one to two weeks if they are able to work while seated. If a person's job requires standing and walking, return to work may take several weeks. Complete recovery may take six months to a full year. Complications can occur as with all surgeries, but are minimized by strictly following your surgeon's post-operative instructions. The main complications include infection, bone that is slow to heal or does not heal, progression or reoccurrence of deformity, a stiff foot, and the need for further surgery. Many of the above complications can be avoided by only putting weight on the operative foot when allowed by your surgeon.

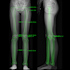

 Interdigital neuroma (Morton?s Neuroma) of the foot includes common, paroxysmal, neuralgia affecting the web spaces of the toes. It involves entrapment neuropathy (nerve compression) of the common digital nerve below and between the metatarsal heads, typically between the third and the fourth metatarsal heads. The pain is most commonly felt between the third and fourth toes but can also occur in the area between the second and third toes.
Interdigital neuroma (Morton?s Neuroma) of the foot includes common, paroxysmal, neuralgia affecting the web spaces of the toes. It involves entrapment neuropathy (nerve compression) of the common digital nerve below and between the metatarsal heads, typically between the third and the fourth metatarsal heads. The pain is most commonly felt between the third and fourth toes but can also occur in the area between the second and third toes.


 Overview
Overview
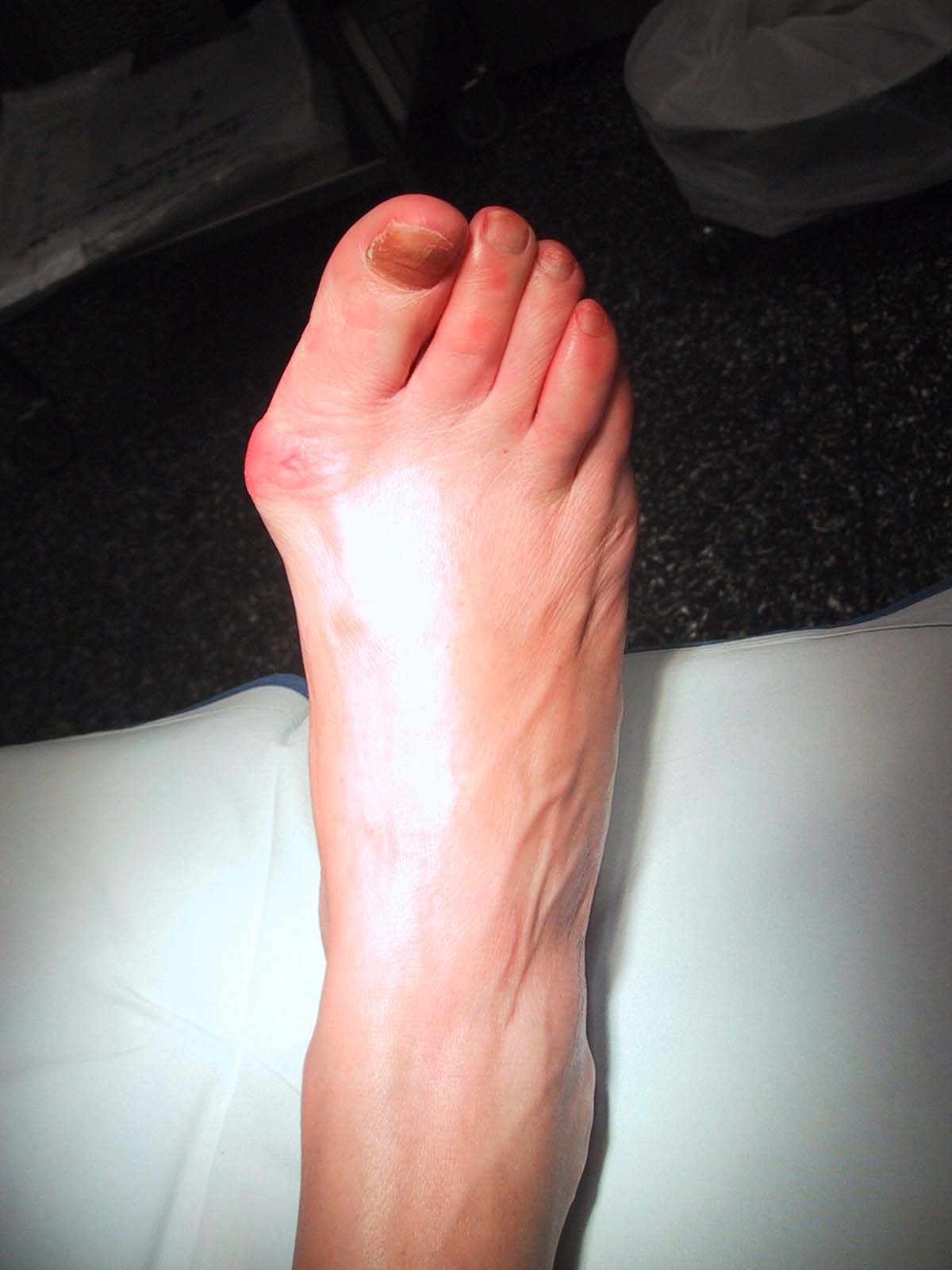
 Though a bunion is often described as a painful bump, this condition is much more complex than a simple bump on the side of the toe. X-rays show the true nature of the deformity and are used to help in the decision making process. Ranges of motion of joints associated with the toe are also performed to assess the deformity. There are many procedures for correcting a bunion and choosing the right one based on the examination increases the chance of success. The procedure performed on one person may not be the procedure required to give another a good result. In general, more severe bunion deformities require more extensive surgery and more extensive post-operative limitations. It is very important to note that the same instability and incorrect motion that causes a bunion also causes degeneration of the joint surfaces (osteoarthritis). Correction of the bunion cannot repair the damage done within the joint and continued pain from that separate process may occur. Realigning the joint may slow the damage within the joint and improve motion, but it may not alleviate all pain.
Though a bunion is often described as a painful bump, this condition is much more complex than a simple bump on the side of the toe. X-rays show the true nature of the deformity and are used to help in the decision making process. Ranges of motion of joints associated with the toe are also performed to assess the deformity. There are many procedures for correcting a bunion and choosing the right one based on the examination increases the chance of success. The procedure performed on one person may not be the procedure required to give another a good result. In general, more severe bunion deformities require more extensive surgery and more extensive post-operative limitations. It is very important to note that the same instability and incorrect motion that causes a bunion also causes degeneration of the joint surfaces (osteoarthritis). Correction of the bunion cannot repair the damage done within the joint and continued pain from that separate process may occur. Realigning the joint may slow the damage within the joint and improve motion, but it may not alleviate all pain.